Understanding flood zone maps is vital for homeowners and borrowers. These maps, created by agencies like FEMA, categorize areas based on risk levels, guiding insurance requirements and lending decisions. Regular updates are crucial for accurate information. By reviewing these maps, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate risks, protect investments, and ensure neighborhood resilience during floods.
In a world where extreme weather events are increasingly frequent, understanding your location’s risk of flooding is more critical than ever for homeowners and consumers. A flood zone map serves as a vital tool, offering crucial insights into these risks, but navigating these resources can be overwhelming. This comprehensive guide breaks down the complexities, demystifying flood zone maps to empower consumers with knowledge. We’ll explore what these maps are, how they’re created, and what they mean for your property, providing an authoritative resource to ensure you make informed decisions in potential high-risk areas.
Understanding Flood Zone Maps: A Beginner's Guide
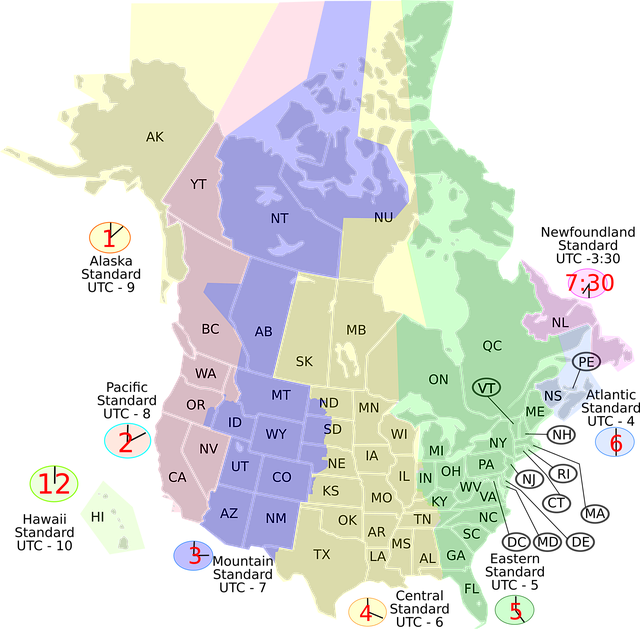
Understanding flood zone maps is a crucial step for anyone considering purchasing property or seeking a loan in potential flood-prone areas. These detailed resources, often referred to as flood zone maps, are designed to help individuals make informed decisions by illustrating areas at risk of flooding based on historical and scientific data. The primary tool for borrowers looking to navigate these risks is the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) map, which categorizes zones according to their likelihood of flooding, from low to high.
For instance, in the United States, the NFIP divides areas into special flood hazard zones, where the risk of flooding is considered significant, and low-risk zones. Lenders are required by law to ensure that borrowers in special flood hazard zones obtain flood insurance as part of their mortgage process (Flood Zone Map Borrower Requirements). This not only protects both the borrower and the lender but also ensures compliance with local regulations. Understanding these maps involves recognizing the different symbols and colors used to represent various flood risks, each corresponding to specific insurance requirements.
While these maps provide a robust framework for assessing flood risks, it’s essential to remember they are based on historical data and models. Changes in climate, urban development, and land use can impact flooding patterns over time. Borrowers should consult the most current maps available from their local government or NFIP to ensure accurate information. Additionally, seeking expert advice from real estate agents or insurance professionals who specialize in flood zones can offer valuable insights tailored to specific locations, providing a comprehensive guide for making informed decisions in potential flood-prone areas.
Interpreting Your Property's Risk: Flood Zone Map Analysis
When reviewing a property, understanding your location in relation to a flood zone map is paramount for any homeowner or borrower. These maps, meticulously crafted by regulatory agencies, offer critical insights into potential flood risks specific to your area. Analysis of this data allows you to make informed decisions regarding insurance requirements and even property value assessments.
The process begins with identifying the relevant flood zone map, often provided by local governments or mapping services. These maps categorise areas based on their susceptibility to flooding events, ranging from high-risk zones (often denoted as Special Flood Hazard Areas) to lower-risk classifications. For instance, in the United States, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) administers such maps, updating them regularly to incorporate new data and changes in topography or land use.
Upon examining your property’s location on the map, borrowers should consider the specific flood zone designation. Properties within high-risk zones may require specialized insurance policies, including Flood Insurance Policies (FIP), which are often mandatory for mortgage lenders. These policies offer financial protection against the potential devastating effects of flooding, a coverage that standard home insurance policies typically do not include. For instance, according to FEMA data, over 14 million properties in the US are located in special flood hazard areas, underscoring the significant impact these maps have on borrowing requirements.
Moreover, understanding your property’s flood risk can influence negotiating power during real estate transactions. Borrowers equipped with this knowledge can make more informed choices regarding down payments or even consider adjusting the property’s value to account for potential insurance costs. Regular updates to flood zone maps are essential for borrowers to stay informed about changes in their area’s risk profile, ensuring they meet the latest lender requirements and protect their investments effectively.
Mitigating Risks: Using Flood Zone Maps for Preparation

Flood zone maps are critical tools for homeowners and prospective buyers alike, offering a clear understanding of areas prone to flooding, which is essential for mitigating risks and making informed decisions. These maps, developed by regulatory agencies and geospatial experts, provide detailed information about floodplains, evacuation routes, and historical flooding data, all of which play a pivotal role in preparing for potential water disasters. By utilizing this resource effectively, individuals can take proactive measures to safeguard their properties and ensure the safety of their families.
For borrowers considering investments in high-risk areas, understanding the dynamics of flood zones is paramount. Lenders often require borrowers to assess these risks before extending credit, as evidenced by recent trends in mortgage underwriting guidelines. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) regularly updates its flood maps, making them readily accessible for public review. These maps can reveal specific flood zones, their severity, and the likelihood of flooding over different time frames, enabling homeowners to make proactive choices like purchasing flood insurance or implementing protective measures on their properties.
For instance, a borrower looking to build a new home in a previously undeveloped area may find that it falls within a Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA), indicating a high risk of flooding. This knowledge prompts them to explore elevation certificates, consult with engineers, and potentially implement floodproofing solutions. By embracing these measures, borrowers can reduce the financial impact of potential floods, ensuring their investments remain secure. Moreover, staying informed about local flood zone maps allows homeowners to stay proactive in community preparedness efforts, fostering a more resilient neighborhood during times of crisis.
Navigating Insurance and Protection: Flood Zone Map Implications
Navigating insurance and protection when considering a property purchase is a crucial aspect of homeownership, especially in areas prone to flooding. The flood zone map serves as a critical tool for borrowers and lenders alike, providing essential insights into potential risks. Understanding this map is paramount to making informed decisions regarding coverage and mitigating financial exposure.
Lenders often require borrowers to review and acknowledge the information presented on these maps before finalizing any loan agreements. The U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) plays a pivotal role in creating and updating these resources, ensuring they reflect the latest data on flood-prone areas. For instance, recent studies have shown that over 13 million properties are located in flood zones across the United States, with this number varying based on changing environmental factors and development patterns. Borrowers should be vigilant in assessing their location’s risk level to determine suitable insurance options.
One of the primary implications for borrowers is the potential impact on insurance costs. Properties situated in higher-risk flood zones may face more stringent insurance requirements, leading to increased premiums. According to a study by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), average annual flood insurance premiums can range from $700 to over $3,000, depending on various factors, including location and property value. Lenders typically mandate flood insurance for borrowers in these areas, ensuring that any potential damage is covered. It’s essential for buyers to engage with reputable insurers who specialize in flood coverage to ensure adequate protection.
Additionally, understanding the flood zone map can help borrowers avoid unexpected financial surprises. Properties located in special flood hazard zones (SFHAs) are subject to more rigorous regulations and may require specific measures to enhance flood resilience. These might include elevation of buildings or installation of water-proof barriers. By proactively addressing these concerns, borrowers can mitigate potential losses and ensure their investment is secure.
